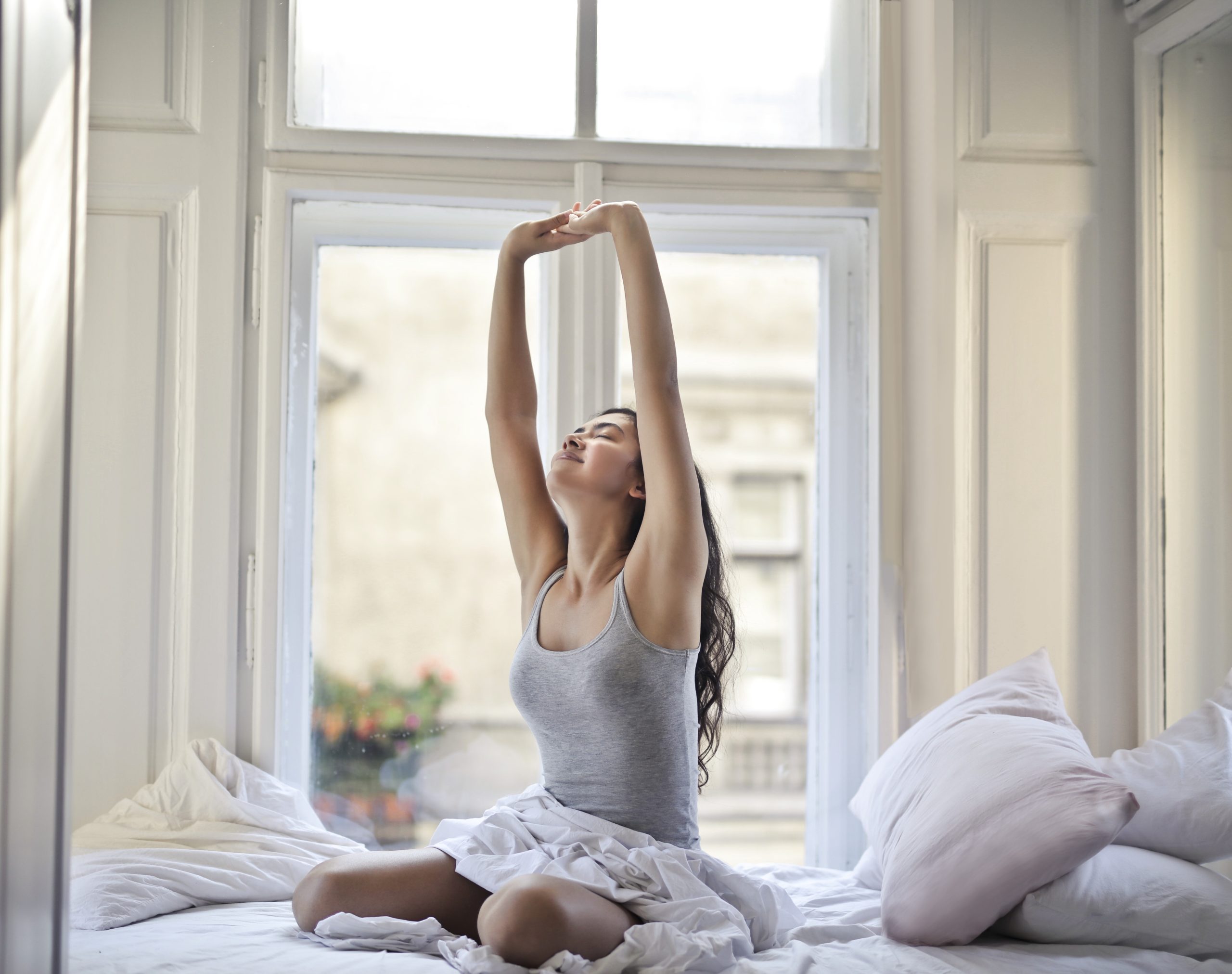
Sleep is a fundamental biological process that allows the body and mind to rest and rejuvenate. It plays a crucial role in maintaining your overall health and well-being, with its impact extending far beyond your physical vitality. In recent years, research has increasingly highlighted the vital connection between sleep and mental health. As well as the significance of sleep in preserving mental health and the adverse consequences of sleep deprivation.
The Role of Sleep. Why is it important?
Sleep is not just a passive state of unconsciousness; it is an active and complex process that contributes significantly to your brain function and mental health. During sleep, your brain undergoes essential processes like memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and problem-solving. Adequate sleep helps to regulate neurotransmitters, hormones, and other chemical messengers that influence mood, stress, and cognitive processes.
Emotional Regulation
One of the most apparent connections between sleep and mental health is the impact on emotional regulation. Sufficient sleep facilitates emotional stability, making it easier to manage stress, anxiety, and emotional upheavals. On the other hand, sleep deprivation can lead to increased emotional reactivity, making people more prone to mood swings and negative emotions.
Cognitive Function
Sleep plays a vital role in your cognitive function and performance. It is crucial for attention, concentration, and learning abilities. A well-rested mind can process information effectively and retain knowledge, which is essential for optimal mental functioning. In contrast, a lack of sleep weakens cognitive abilities, affecting memory, decision-making, and problem-solving skills.
The Vicious Cycle of Sleep Deprivation and Mental Health
Sleep deprivation can lead to a vicious cycle that negatively impacts mental health. For example, stress, anxiety, or depression can cause sleep disturbances, and in turn, sleep deprivation worsens these mental health issues. Breaking this cycle is essential to promote mental well-being.
Sleep Hygiene
To harness the benefits of sleep for mental health, practicing good sleep hygiene is essential. Sleep hygiene refers to adopting habits and practices that promote healthy sleep patterns. Some key aspects include maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a conducive sleep environment, limiting exposure to electronic devices before bedtime, and avoiding stimulants like caffeine and nicotine close to sleep time.
Seeking Professional Help
In cases where you, or someone you know, experience chronic sleep problems or mental health issues, seeking professional help is crucial. Mental health professionals can assess and treat sleep disorders and related mental health conditions. They may recommend therapies, medication, or lifestyle changes to improve sleep quality and overall mental well-being.
Sleep is a fundamental pillar of mental health and well-being. The relationship between sleep and mental health is bidirectional, with each influencing the other significantly. Prioritizing and maintaining adequate, restorative sleep should be seen as an essential aspect of self-care and mental health maintenance. By recognizing the importance of sleep and adopting healthy sleep habits, we can take proactive steps towards nurturing a healthier mind and a more fulfilling life.